The Race to Store the Future: Why the World Is Betting Big on Clean Energy Storage
As solar panels stretch across deserts and wind turbines pierce the skies, a quieter yet more urgent revolution is brewing beneath the surface: energy storage.
From Washington to Abu Dhabi, the real challenge of clean energy isn’t just how to generate it—it’s how to store it.
Global Stakes, National Moves
As the climate clock ticks and pressure mounts to move beyond fossil fuels, countries are now channeling major resources into energy storage solutions.
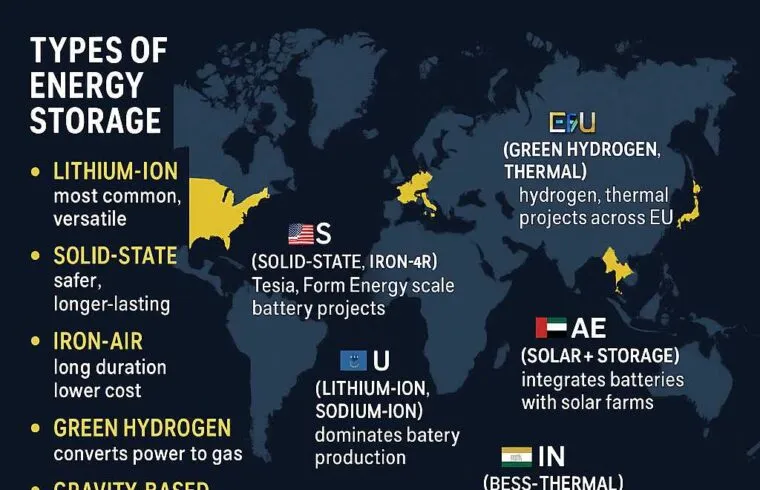
United States
Backed by the Inflation Reduction Act, the U.S. has committed billions to develop cutting-edge battery systems. Companies like Tesla and Form Energy are pioneering scalable, long-duration storage technologies such as iron-air batteries—offering potential to store energy for up to 100 hours.
China
Dominating lithium-ion battery production, China is rapidly transitioning toward sodium-ion batteries, which offer a safer, cheaper alternative. As of 2025, several Chinese battery megafactories are online, linked directly to solar farms.
Europe
Germany, Sweden, and the UK are focusing heavily on green hydrogen and thermal storage. Germany is leading with its ambitious hydrogen infrastructure, while the UK is investing in gravity-based energy systems built into disused mining shafts.
UAE & the Middle East
The UAE is positioning itself as a leader in solar-plus-storage integration, pairing large-scale solar projects with grid-connected battery packs such as Tesla Megapack units. Saudi Arabia’s $500B NEOM city plans to operate on 100% renewable energy supported by hydrogen and thermal storage.
India
India is emerging as a manufacturing hub for battery cells and is integrating Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) across its major solar parks. Additionally, pilot projects in rural states are testing thermal storage using sand and salt beds—low-cost but effective.
The Tech Toolbox: More Than Just Batteries
While lithium-ion technology remains the most visible solution, the field of storage is rapidly diversifying:
- Solid-State Batteries: Non-flammable, faster-charging, and longer-lasting. Still experimental but promising for mass market use.
- Iron-Air Batteries: Store electricity by rusting and unrusting iron. Cheap, abundant, and ideal for multi-day storage.
- Green Hydrogen: Splits water using renewable power, storing energy in gas form for months.
- Gravity Storage: Uses excess energy to lift weights. When dropped, the falling mass spins a generator.
- Thermal Storage: Stores heat in materials like molten salt or bricks. Converts back into energy when needed.
- Sodium-Ion Batteries: A lower-cost, safer cousin to lithium-ion, ideal for shorter cycles and developing markets.
These diverse approaches reflect one truth: no single solution will fit all needs. Storage must be adapted regionally, just as generation has been.
The Urgency: Why the Push Can’t Wait
Governments and scientists agree—without energy storage, the transition to net-zero is impossible.
- Climate deadlines loom: Net-zero targets for 2050 are non-negotiable.
- Wasted renewable energy is common: On sunny or windy days, gigawatts go unused due to lack of storage.
- Grid instability is increasing: Wildfires, floods, and storms now threaten electricity access.
- Geopolitical energy crises: The war in Ukraine and Middle East volatility show why energy independence matters.
Editorial Perspective
This is not just a tech race. It’s a global survival strategy. Energy storage is the missing link between climate goals and a livable future.
If clean energy is the vehicle, storage is the engine that keeps it running—even at night, during storms, and across continents.
It’s time the world pays as much attention to saving power as it does to making it.
Key Takeaways
- Energy storage is now a national priority across the globe.
- New tech—from iron-air batteries to thermal sand beds—is reshaping how we store electricity.
- Time is short, but investments are growing fast.